Intro paragraph:
Hyperopia, commonly known as farsightedness, is a vision condition that affects millions of people worldwide. If you have trouble seeing objects up close but can see distant objects clearly, you might be experiencing hyperopia. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is essential for maintaining healthy vision.
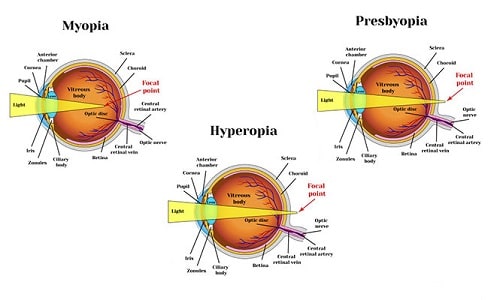
What is Hyperopia?
Hyperopia occurs when the eye focuses images behind the retina instead of directly on it. This usually happens because the eyeball is shorter than normal or the cornea has too little curvature. As a result:
-
Close objects appear blurry
-
Distant objects may be seen more clearly
-
Eyes work harder to focus, causing strain
Farsightedness can affect children and adults and may worsen with age.
Common Symptoms of Hyperopia
It can be easy to overlook mild hyperopia because the eyes often compensate. However, as the condition progresses, common symptoms include:
-
Blurry vision when reading or doing close-up work
-
Eye strain or fatigue
-
Headaches after prolonged near tasks
-
Squinting to see clearly
-
Difficulty focusing on smartphones, books, or computer screens
Children may not realize their vision is blurry, which is why regular eye exams are important.
Causes of Hyperopia
The primary causes include:
-
Shorter-than-normal eyeball – prevents light from focusing correctly
-
Flat cornea – reduces focusing power
-
Age-related changes – lens flexibility decreases over time
Genetics also play a role; if parents are farsighted, children may be more likely to develop hyperopia.
How to Diagnose Hyperopia
Only a professional eye exam can confirm hyperopia. Your eye doctor may perform:
-
Visual acuity tests – reading letters on a chart
-
Refraction test – determines the correct lens prescription
-
Comprehensive eye exam – checks overall eye health
Early detection is important, especially for children, to prevent strain or vision problems that can affect learning.
Treatment Options
Hyperopia can be managed and corrected with several methods:
1. Eyeglasses
The most common solution for farsightedness. Lenses help focus light directly onto the retina, improving near vision.
2. Contact Lenses
Soft or rigid gas-permeable lenses can correct hyperopia. Daily or extended wear options are available.
3. Refractive Surgery
Procedures like LASIK or PRK reshape the cornea to correct focusing issues. Not everyone is a candidate, so a consultation with an eye surgeon is necessary.
4. Vision Therapy
In some cases, especially for children, vision exercises may help improve focusing ability and reduce eye strain.
Preventing Eye Strain with Hyperopia
Even with correction, it’s important to reduce eye fatigue:
-
Take regular breaks when reading or using screens (20-20-20 rule)
-
Maintain proper lighting
-
Use ergonomic setups for computers and study areas
-
Stay hydrated and get enough sleep
When to See an Eye Doctor
Seek professional help if you experience:
-
Persistent blurry vision up close
-
Frequent headaches after near tasks
-
Difficulty reading or using digital devices
-
Eye strain or discomfort
Early detection ensures proper treatment and reduces long-term complications.
Conclusion
Hyperopia, or farsightedness, is common but manageable. Recognizing the signs and seeking proper care from an eye specialist can help you maintain clear vision and prevent discomfort. Whether through glasses, contact lenses, or surgery, corrective options exist for every lifestyle—so you can see your world clearly, near and far.
Make your appointment today
To make your appointment, simply give us a call (760)-948-3345 or
or
At Golden Eye Optometry, we view good vision care as front line protection at every age. A routine eye exam can detect more than poor vision. It can shed early light on glaucoma, macular degeneration, cataracts and diabetes.
Information received through Golden Eye Optometry social media channels is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice, medical recommendations, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your eye doctor, physician, or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.